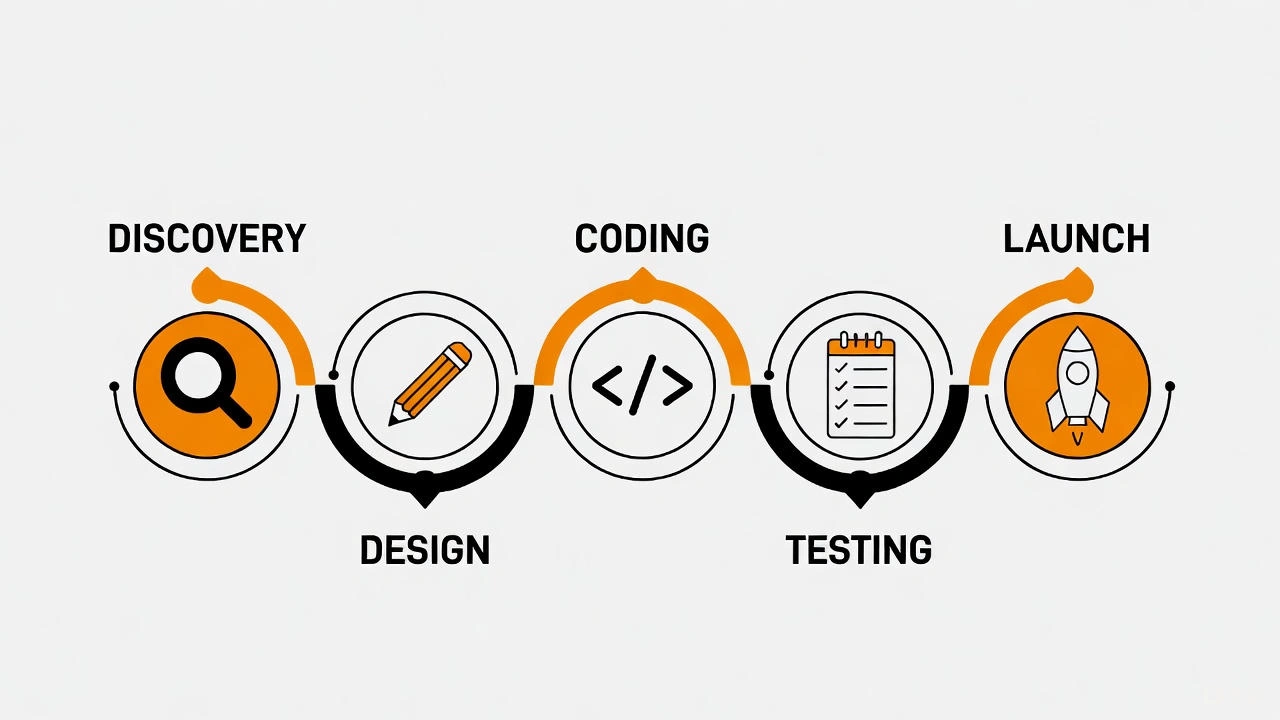
Turning a great idea into a successful mobile app involves much more than just writing code. It requires a structured, multi-stage process known as the mobile app development lifecycle.
This framework guides your project from a simple concept to a fully functional application on users’ devices. Understanding these mobile app development phases is crucial for saving time, managing budgets, and ultimately, building a product that people love to use.
This guide will walk you through each step of the journey. We will explore the critical stages, from initial strategy and planning to post-launch maintenance, providing a clear roadmap for your development process.
What is the Mobile App Development Lifecycle?
The mobile app development lifecycle is a systematic process that outlines the steps required to build and launch a mobile application. It acts as a project management blueprint, ensuring that every aspect of development is covered logically and efficiently.
By following this lifecycle, development teams can minimize risks, align with stakeholder expectations, and maintain quality throughout the project.
Think of it as the recipe for creating a successful app… without it, you risk ending up with a jumble of ingredients instead of a finished dish.
Phase 1: Strategy and Discovery
Before a single line of code is written, a solid strategy must be in place. The discovery phase is arguably the most critical part of the entire lifecycle, as it lays the foundation for everything that follows. Rushing this stage often leads to costly mistakes later on.
Defining the “Why”
The first step is to clarify the app’s core purpose. Ask yourself and your team some fundamental questions:
- What problem does this app solve for users?
- Who is the target audience?
- What are the primary business goals (e.g., revenue generation, brand building, improving efficiency)?
- How will we measure success?
Competitive Analysis
Next, you need to understand the market. Research existing apps in your niche to identify their strengths and weaknesses. This analysis helps you find opportunities to differentiate your product. Look for gaps in the market or areas where competitors fall short. This insight allows you to create a unique value proposition that will make your app stand out.
Finalizing the Concept and MVP
Based on your research, you can refine your app idea. At this stage, it’s wise to define the scope of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). An MVP includes only the essential features needed to solve the core problem for your initial users. This approach allows you to launch faster, gather real-world feedback, and make informed decisions for future updates, controlling the initial mobile app development timeline and budget.
Phase 2: Planning and Analysis
With a clear strategy, you can move into detailed planning. This phase involves translating your ideas into concrete requirements and creating a project roadmap.
Requirement Gathering
Here, you’ll document the specific functionalities and technical requirements of the app. This involves creating detailed use cases and user stories. For example, a user story might look like: “As a new user, I want to be able to sign up with my email address so I can create a profile.” This process ensures everyone on the team, from developers to designers, has a shared understanding of what needs to be built.
Choosing the Technology Stack
A crucial decision in the planning phase is selecting the right technology. This choice depends on your target platforms (iOS, Android, or both), budget, and desired app performance.
- Native Apps: Built specifically for one platform (iOS or Android) using platform-specific languages like Swift/Objective-C for iOS and Kotlin/Java for Android. Native apps offer the best performance and user experience.
- Hybrid Apps: Developed using web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and wrapped in a native container. Frameworks like Ionic and Cordova allow you to write code once and deploy it on multiple platforms, but performance might be compromised.
- Cross-Platform Apps: Built with frameworks like React Native or Flutter. These offer a balance between native performance and development efficiency, allowing a single codebase to be used for both iOS and Android.
Creating a Project Roadmap
The final part of this phase is to establish a detailed mobile app development timeline. This involves breaking down the project into smaller tasks, assigning them to team members, and setting deadlines for each milestone. This roadmap will guide the project and help track progress against your goals.
Phase 3: UI/UX Design
This phase is all about how the app looks and feels. Great UI/UX design is essential for user retention. If an app is confusing or difficult to navigate, users will quickly abandon it. The design phase typically has two main components: User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI).
User Experience (UX) Design
UX design focuses on the overall feel and logic of the app. The goal is to create a seamless and intuitive journey for the user. UX designers build wireframes, which are basic black-and-white blueprints of the app’s structure. These wireframes map out the user flow and screen layouts without any visual design elements. This allows the team to focus purely on functionality and navigation before adding color and style.
User Interface (UI) Design
Once the wireframes are approved, UI designers step in to bring the app to life visually. UI design is concerned with the look of the app, including color schemes, typography, buttons, icons, and animations. The UI designer creates high-fidelity mockups, which are static images that represent the final look of the app. They also create a style guide to ensure visual consistency across all screens.
Prototyping
The final step in the design phase is creating an interactive prototype. This is a clickable simulation of the app that allows stakeholders and test users to experience the user flow and provide feedback before development begins. Prototypes are invaluable for identifying usability issues early, saving significant time and resources during the development stage.
Phase 4: App Development
This is where the magic happens. The development team takes the designs and technical specifications from the previous phases and starts building the actual application. This phase is often the longest in the mobile app development lifecycle.
The development process is typically broken down into three parts:
- Back-End Development: This involves building the server-side components that support the app’s functions. This includes databases, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), and server logic. The back-end handles tasks like user authentication, data storage, and push notifications.
- API Integration: The API acts as the bridge between the back-end and the front-end. Developers ensure that the mobile app can communicate effectively with the server to send and receive data.
- Front-End Development: This is the client-side development, focusing on what the user actually sees and interacts with. Front-end developers take the UI mockups and build the interactive user interface, connecting it to the back-end via the API.
Development is often managed using agile methodologies, where the project is broken into short cycles called “sprints.” At the end of each sprint, the team delivers a small, functional piece of the app, allowing for continuous feedback and adjustments.
Phase 5: Testing and Quality Assurance
Once the app is built, it must be thoroughly tested to ensure it is stable, secure, and bug-free. The Quality Assurance (QA) phase is critical for delivering a polished and reliable product. Testing covers several areas:
- Functional Testing: Verifying that all features work as specified in the requirements document.
- Usability Testing: Ensuring the app is easy to navigate and provides a positive user experience.
- Performance Testing: Checking the app’s speed, responsiveness, and battery consumption under various conditions.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the app works correctly on different devices, screen sizes, and operating system versions.
- Security Testing: Identifying and fixing potential vulnerabilities that could compromise user data.
Rigorous testing helps catch issues before the app reaches users, preventing negative reviews and protecting your brand’s reputation.
Phase 6: Deployment and Launch
After the app has passed all testing stages and received final approval, it’s time to launch it to the public. This involves submitting the app to the respective app stores—the Apple App Store for iOS and the Google Play Store for Android.
Each store has its own submission guidelines and review process. You’ll need to prepare metadata for your app store listing, including:
- App Name
- Description
- Icon
- Screenshots and a preview video
- Keywords
The review process can take anywhere from a few hours to several days. Once approved, your app will be live and available for users to download.
Phase 7: Post-Launch Maintenance and Updates
The mobile app development lifecycle doesn’t end at launch. In fact, the work is just beginning. The post-launch phase is about monitoring, maintaining, and improving your app over time.
Monitoring
Continuously monitor your app’s performance using analytics tools. Track key metrics like downloads, user engagement, crash reports, and user feedback. This data provides valuable insights into how people are using your app and what needs improvement.
Maintenance and Updates
Based on monitoring and user feedback, you’ll need to release regular updates. These updates can include bug fixes, performance enhancements, and new features. Keeping your app updated is essential for retaining users and staying competitive. It also ensures your app remains compatible with the latest versions of iOS and Android.
Conclusion
The mobile app development lifecycle provides a proven framework for taking an app from concept to reality and beyond. By following these structured mobile app development phases… from strategy and planning to deployment and maintenance… You can streamline your process, mitigate risks, and build a high-quality product that meets both business goals and user needs. Understanding this lifecycle is the first step toward a successful and sustainable mobile application.
 ?>
?>
 ?>
?>

 ?>
?>
 ?>
?>