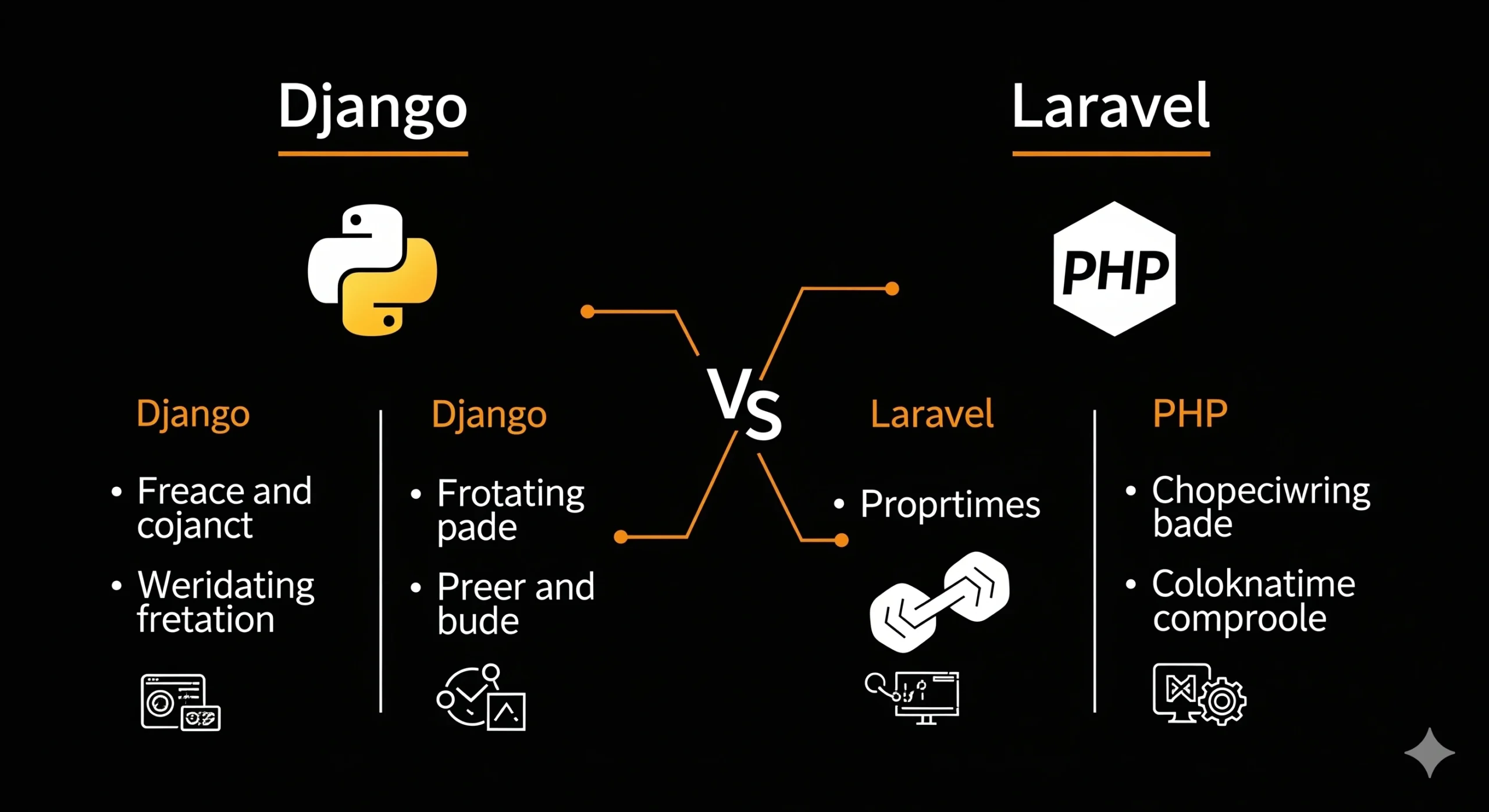
Choosing between Django vs Laravel is one of the first decisions you make for a web project. Both are mature, well supported, and able to build production-grade apps.
The right choice depends on the project, the team, and non-technical factors like hosting and maintenance. This guide explains both frameworks clearly, compares them side by side, gives real-world use cases, and offers step-by-step guidance so you can decide with confidence.
Quick overview: what are Django and Laravel?
Django
- Language: Python
- Architecture: Model View Template (MVT)
- First released: 2005
- Strengths: built-in admin, batteries-included approach, strong security defaults, great for data-heavy apps and fast MVPs.
Laravel
- Language: PHP
- Architecture: Model View Controller (MVC)
- First released: 2011
- Strengths: elegant syntax, rich ecosystem of packages, strong tooling for queues, jobs and APIs, fast developer experience for typical web apps and CMS.
- It is also a complete package of full-stack development based on PHP language.
Head-to-head at a glance (quick comparison)
| Topic | Django | Laravel |
| Language | Python | PHP |
| Architecture | MVT | MVC |
| Admin UI | Built-in admin site | No built-in admin, Nova paid option |
| ORM | Django ORM | Eloquent ORM |
| API support | Django REST Framework (very popular) | Laravel Sanctum / Passport, API resources |
| Background jobs | Celery (common) | Queues, Horizon |
| Performance tuning | Gunicorn, ASGI, caching | Octane (Swoole/RoadRunner), caching |
| Security | Strong defaults (CSRF, XSS protections) | Strong features, good community best practices |
| Learning curve | Moderate, good for Python devs | Easy to moderate for PHP devs |
| Best for | Data-driven apps, complex back ends | Rapid web apps, eCommerce, CMS, APIs |
| Community & packages | Large Python ecosystem | Large PHP ecosystem, many Laravel packages |
Why this comparison matters (real value)
- Maintenance and longevity. The framework you pick affects how easy it is to update dependencies, onboard new developers, and keep security up to date.
- Speed to market. Frameworks with richer built-in tooling reduce boilerplate and accelerate delivery.
- Operational cost. Python and PHP hosting are widely available, but server choices and scaling patterns differ.
- Fit with team skills. If your engineers know Python, Django will be faster to adopt, and the same goes for PHP and Laravel.
Real-world use cases and tools
When to use Django
- Complex, data-driven platforms where Python’s libraries (data, ML, analytics) help.
- Apps that benefit from an auto-generated admin panel and strong built-in security.
- Projects that will integrate data science or heavy backend logic.
Common tools
- Django REST Framework (API)
- Celery (background tasks)
- Channels / ASGI (websockets, async)
- Gunicorn, Nginx (deployment)
- PostgreSQL or MySQL
When to use Laravel
- Rapid web apps, content sites, and ecommerce.
- Projects that need elegant developer tooling, artisan CLI, and fast iteration.
- APIs and microservices where PHP is already in use.
Common tools
- Eloquent ORM
- Horizon (queue dashboard), Octane (performance), Forge (server provisioning), Vapor (serverless)
- Passport / Sanctum (auth for APIs)
- Composer for package management
Traditional vs modern approach
Traditional PHP sites were often built with scripts and mixed logic and presentation. Modern frameworks like Laravel enforce architecture, separation of concerns, and provide tooling for testing, deployment, and security.
Traditional Python web apps sometimes used simple WSGI frameworks or CGI scripts. Django brought a full-stack, batteries-included approach that standardizes how apps are built.
Modern frameworks focus on:
- clear structure and maintainability
- integrated security measures
- modular components and package ecosystems
- built-in testing and CI friendliness
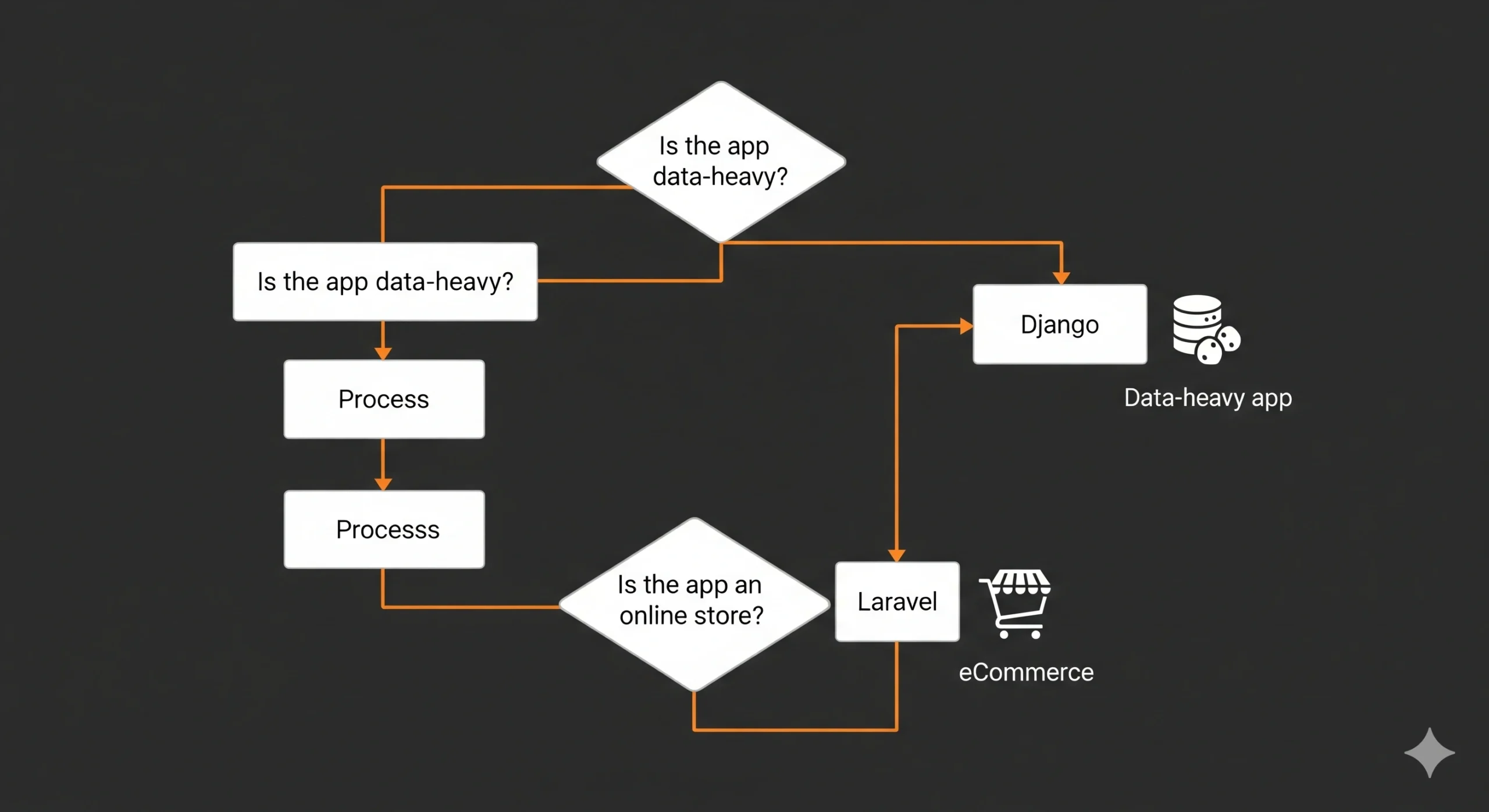
How to choose — step-by-step decision guide
-
Define the project type
- Data heavy, machine learning, analytics: favor Django.
- CMS, ecommerce, typical CRUD apps: favor Laravel.
-
Check team skills
- If you have Python developers, Django reduces ramp-up time.
- If your team is PHP-savvy, Laravel speeds development.
-
Consider third-party needs
- Need an admin UI out of the box? Django wins.
- Need Laravel-specific integrations (Forge, Vapor, Nova)? Laravel wins.
-
Think about hosting and ops
- Standard Linux hosting supports both. For serverless or Swoole-based performance, Laravel has first-class options.
-
Estimate long-term maintenance
- Which community libraries does your app depend on? Check project health, release cadence, and security track record.
-
Prototype quickly
- Build a small feature or MVP in each, then compare speed, developer comfort, and runtime metrics.
Best practices for Django projects
- Use virtual environments and pin dependencies in requirements.txt or Pipfile.
- Use Django REST Framework for APIs.
- Offload background jobs to Celery or built-in async features when needed.
- Configure secure production settings: strong SECRET_KEY, secure cookies, HTTPS.
- Use migrations for database changes and automated tests for regressions.
- Deploy with Gunicorn and Nginx, add caching (Redis) and connection pooling.
Best practices for Laravel projects
- Manage dependencies with Composer and use Laravel Mix for asset compilation.
- Use Eloquent relationships properly to avoid N+1 queries; use eager loading.
- Use queues and Horizon to process heavy tasks.
- Cache routes, config, and views in production for performance.
- Use built-in testing with PHPUnit or Pest for regression checks.
- Consider Octane for performance-sensitive apps but profile carefully.
On the other hand, the Laravel system is also a web-based platform with easy coding and various available tools/features that are enough for a complex web application. Laravel advanced features are including routing tools, session, and security features.
Migration and interoperability notes

- Migrating a live app from Django to Laravel usually means a full rewrite because they use different languages and ecosystems.
- If you need interoperability, build language-agnostic APIs (JSON REST or gRPC) so services can use different stacks but communicate cleanly.
- When replatforming, plan for data migration, contract testing between services, and a phased cutover to limit risk.
Cost, hiring, and community
- Developer availability. PHP developers are widely available, and Laravel is very popular in the PHP space. Python developers are in high demand too, particularly for data roles.
- Ecosystem costs. Some Laravel tools like Nova are paid. Django offers many free, open-source packages.
- Community support. Both frameworks have strong communities, plentiful tutorials, and active forums.
Quick comparison: performance and security
- Performance depends more on app design and deployment than the framework alone. Use caching, optimized queries, and proper server configuration.
- Security Both frameworks provide protections (CSRF, XSS, SQL injection prevention). Django ships with many secure defaults. Laravel provides secure helpers and recommended practices. Follow the official guides and keep dependencies up to date.
FAQ
Which is better, Django or Laravel?
There is no universal better framework. Use Django for Python-based, data-heavy apps. Use Laravel for PHP-based web applications and fast iteration.
Is Django faster than Laravel?
Speed depends on the use case. Well-configured apps in either framework perform well. Measure with real workloads.
Can I use Django for APIs?
Yes. Django REST Framework is the standard choice for building robust APIs with Django.
Is Laravel good for enterprise projects?
Yes. Laravel scales well for many enterprise use cases, especially with queues, caching, and good architecture.
How hard is it to switch frameworks later?
Switching languages and frameworks often requires a rewrite. Design your system with modular services if you might switch in the future.
Final recommendation and next steps
- If your project ties into Python data tooling, machine learning, or you want a ready-made admin and strong security defaults, choose Django.
- If you want fast developer workflows, elegant syntax, and a rich PHP ecosystem for CMS and ecommerce, choose Laravel.
- If you are unsure, build a one-week prototype of core features in the preferred framework and measure development speed and runtime behavior.
Need help deciding for a specific project? Share your project goals, expected traffic, and the team’s skill set. Virtuenetz provides expert web development and migration services to ensure a smooth transition and scalable growth for your business.
 ?>
?>
 ?>
?>
 ?>
?>
 ?>
?>
 ?>
?>